Imagine having access to some of the most powerful computers in the world—without ever needing to buy or maintain them. That’s the magic of Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)! Whether you’re streaming your favorite show, collaborating on a document, or running a business, chances are you’re using the cloud. But what exactly is a CSP, and why does it matter?
What Is a Cloud Service Provider (CSP)?
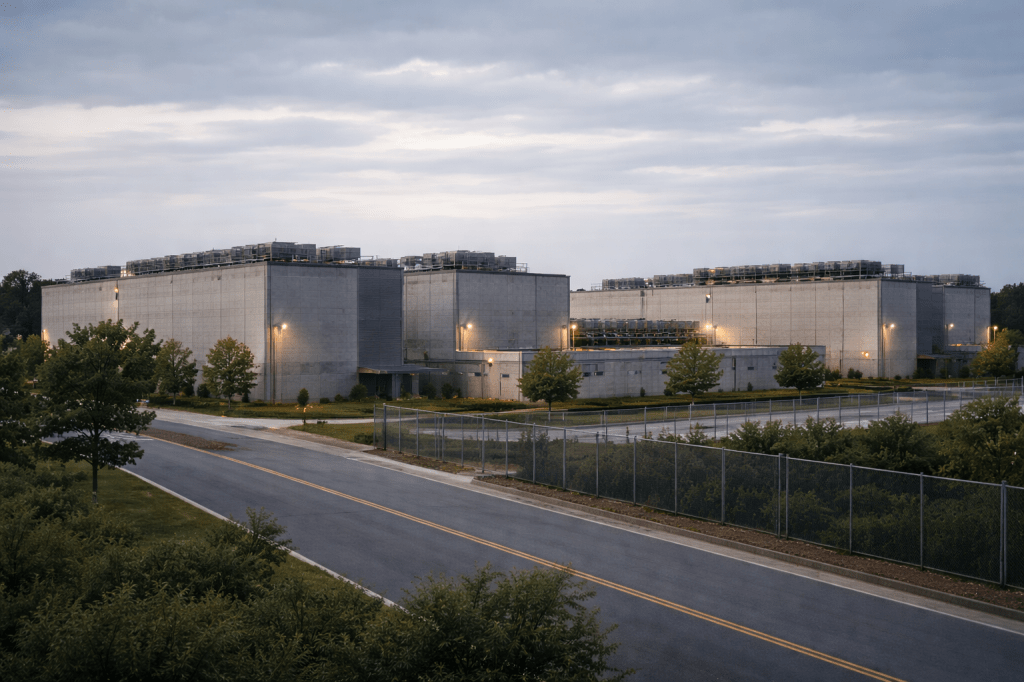
A Cloud Service Provider (CSP) is a company that delivers computing resources—like storage, networking, virtual machines, and software—over the Internet. Instead of owning massive data centers filled with expensive hardware, businesses and individuals can rent what they need from a CSP. These providers operate enormous, high-tech facilities equipped with powerful servers and networking infrastructure to ensure fast, reliable, and scalable cloud services.
The Big Three: Leading Cloud Providers
When it comes to cloud computing, three giants dominate the industry:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – The industry leader, powering companies like Netflix and Airbnb.
- Microsoft Azure – A favorite among enterprises, especially those already using Microsoft products.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – Known for its powerful analytics and machine learning capabilities.
The Three Core Cloud Services
CSPs offer different types of cloud services, categorized into three main models:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Think of IaaS as renting the building blocks of computing—virtual servers, storage, and networking—without owning physical hardware. You can create and manage your own IT environment on demand.
Example: Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), which provides virtual machines for running applications.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS goes one step further by providing developers with a platform to build, deploy, and manage applications—without worrying about the underlying hardware or software maintenance.
Example: Cloud-based application platforms like Google App Engine allow developers to create apps without dealing with server management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
With SaaS, users can access software applications over the Internet without installing anything on their devices. These apps are maintained and updated by the provider, making life easier for businesses and individuals.
Example: Email services like Gmail, Outlook, and even the nostalgic AOL Mail (“You’ve got mail!”).
Why Use Cloud Computing? The Big Benefits
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we work and interact with technology. Here are three key benefits:
1. Accessibility—Work from Anywhere
With cloud-based services, you can access your files, applications, and systems from anywhere with an Internet connection. Remote work and collaboration have never been easier.
2. Cost Savings—Pay for What You Use
Instead of purchasing expensive hardware upfront, CSPs operate on a pay-as-you-go model. You only pay for the resources you use, making cloud computing a cost-effective solution for businesses and individuals alike.
3. High Availability—Minimal Downtime
CSPs ensure that cloud services remain online and reliable. Availability is measured in nines—for example, “four nines” (99.99%) means less than an hour of downtime per year. That’s much more reliable than a traditional on-premise setup.
The Cloud Is Just Someone Else’s Computer… Or Is It?
You may have heard the joke: “The cloud is just someone else’s computer.” While that’s technically true, CSPs provide far more than just storage. They offer cutting-edge computing power, security, and innovation at a scale that individual users and companies could never achieve on their own.
So, whether you’re streaming, coding, gaming, or managing a business—welcome to the cloud. It’s where the future is built! 🚀 big computer. Cloud Service Providers are simply providing us with the most powerful computers in the world.







Leave a comment